Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH): role, symptoms of blood imbalance and normality
1. The role of ACTH in the body
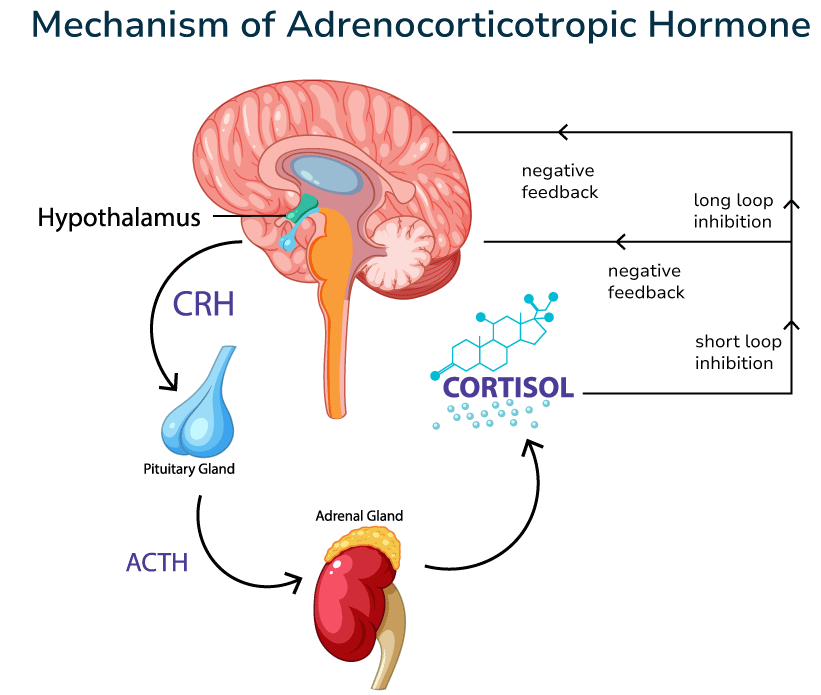
ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone) is a hormone produced by the anterior pituitary gland under the control of the hypothalamus (via corticoliberin, CRH).
Main functions:
✔ Adrenal Stimulation – ACTH causes the adrenal cortex to produce:
- Cortisol (a glucocorticoid that regulates metabolism and stress response).
- Androgens (precursors of sex hormones).
- To a lesser extent – aldosterone (a mineralocorticoid that controls the water-salt balance).
✔ Maintaining circadian rhythms – ACTH levels are maximal in the morning (6-8 hours) and minimal in the evening.
✔ Participation in the stress response – under stress (physical or emotional), ACTH secretion increases dramatically.
2. Symptoms of ACTH deficiency (hypocorticism)
Reasons:
- Hypopituitarism (pituitary insufficiency due to a tumor, injury, or ischemia).
- Long-term use of glucocorticoids (suppresses the production of ACTH on the feedback principle).
- Sheehan’s syndrome (postpartum pituitary necrosis).
Symptoms:
- Chronic weakness, fatigue (due to lack of cortisol).
- Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar).
- Weight loss, lack of appetite.
- Hypotension (low blood pressure).
- Pallor of the skin (due to a decrease in ACTH and melanocyte-stimulating hormone).
3. Symptoms of excess ACTH (hypercorticism)
Reasons:
- Itsenko-Cushing ‘s disease(pituitary adenoma, excessively producing ACTH).
- Ectopic production of ACTH (in small cell lung cancer, carcinoids).
- Adrenal insufficiency (the adrenal glands do not respond to ACTH — > compensatory growth of ACTH).
Symptoms:
- Obesity with fat deposition on the face (‘moon face’), stomach, neck.
- Stretch marks (striae) purple color on the skin.
- Arterial hypertension (high blood pressure).
- Osteoporosis (brittle bones).
- Hirsutism and acne (due to excess androgens).
- Impaired glucose tolerance (prediabetes).
4. Norms of ACTH in the blood test
ACTH levels fluctuate strongly throughout the day:
| Time to submit the analysis | Reference values (pg / ml) |
|---|---|
| Morning (7: 00-10: 00) | 7-63 (maximum level) |
| Evening (18: 00-22: 00) | < 30 (minimum level) |
Important:
- The test is taken strictly on an empty stomach, in the morning, at rest (stress distorts the result).
- At the same time, cortisol is checked for a comprehensive assessment.
5. When is an ACTH test scheduled?
- Suspected Itsenko-Cushing’s disease / syndrome.
- Diagnosis of adrenal insufficiency (Addison’s disease).
- Evaluation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis.
- Control of long-term glucocorticoid therapy.
In case of abnormalities , an endocrinologist’s consultation and additional tests (corticoliberin test, pituitary MRI) are required.
Добавить комментарий